Visualizza Tutti
BEV
HYBRID
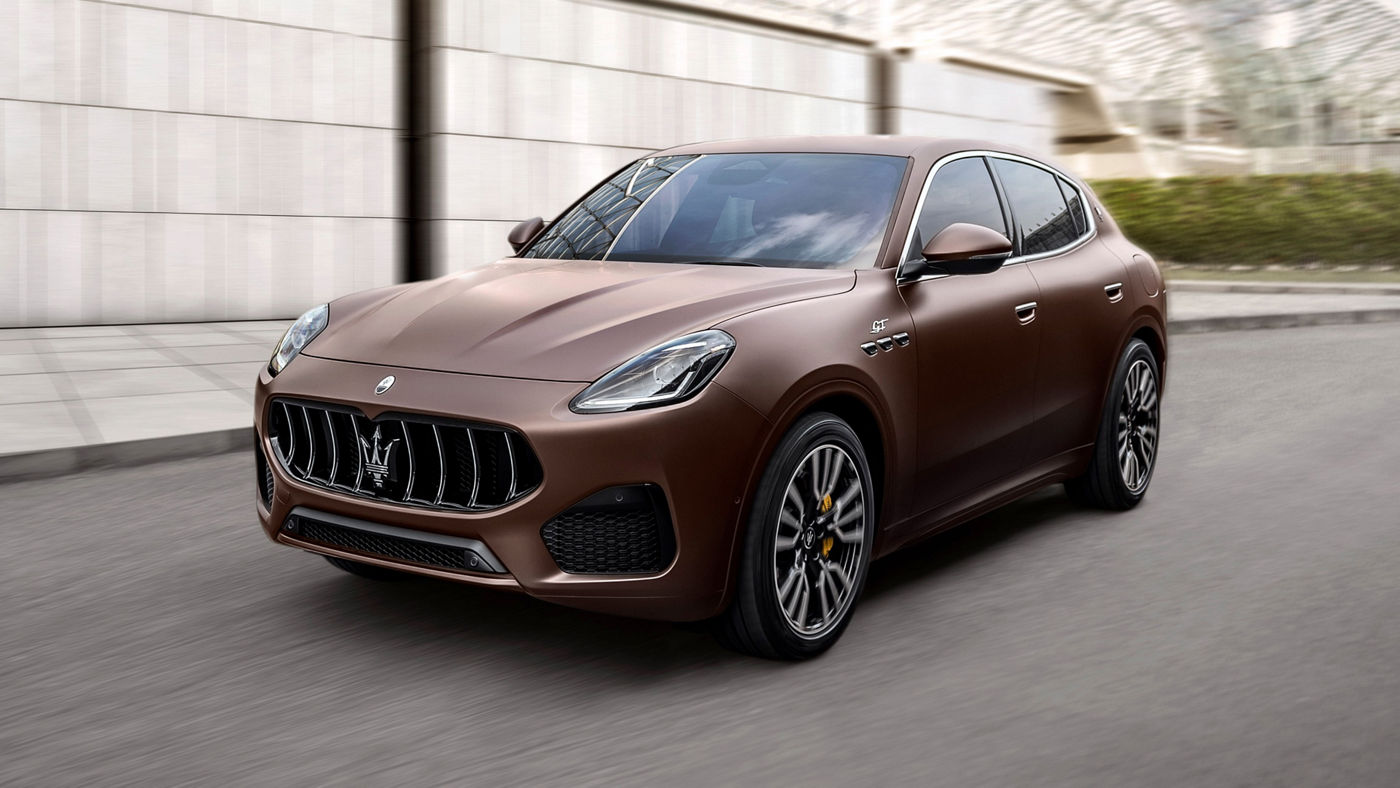
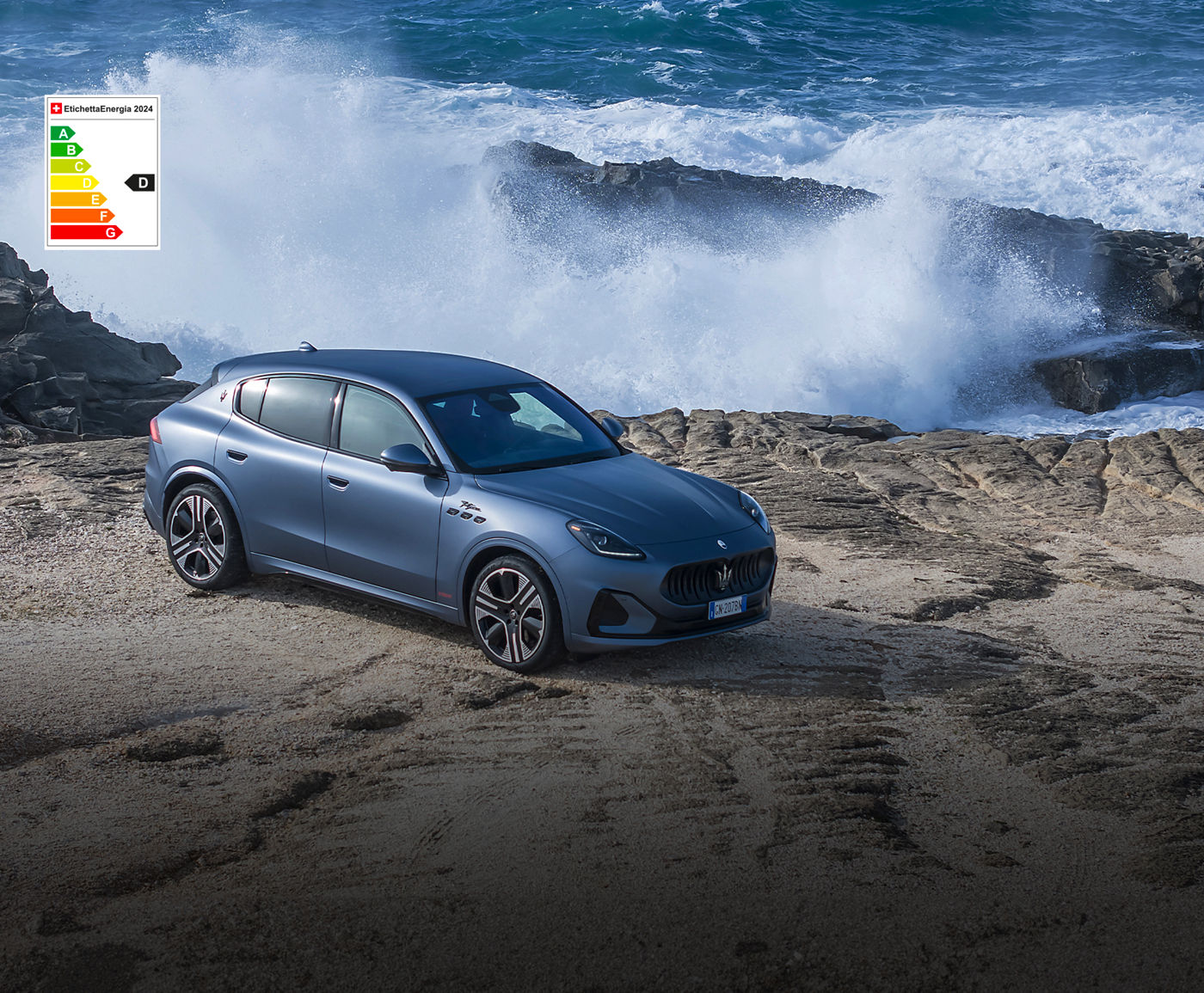
Grecale
Ghibli
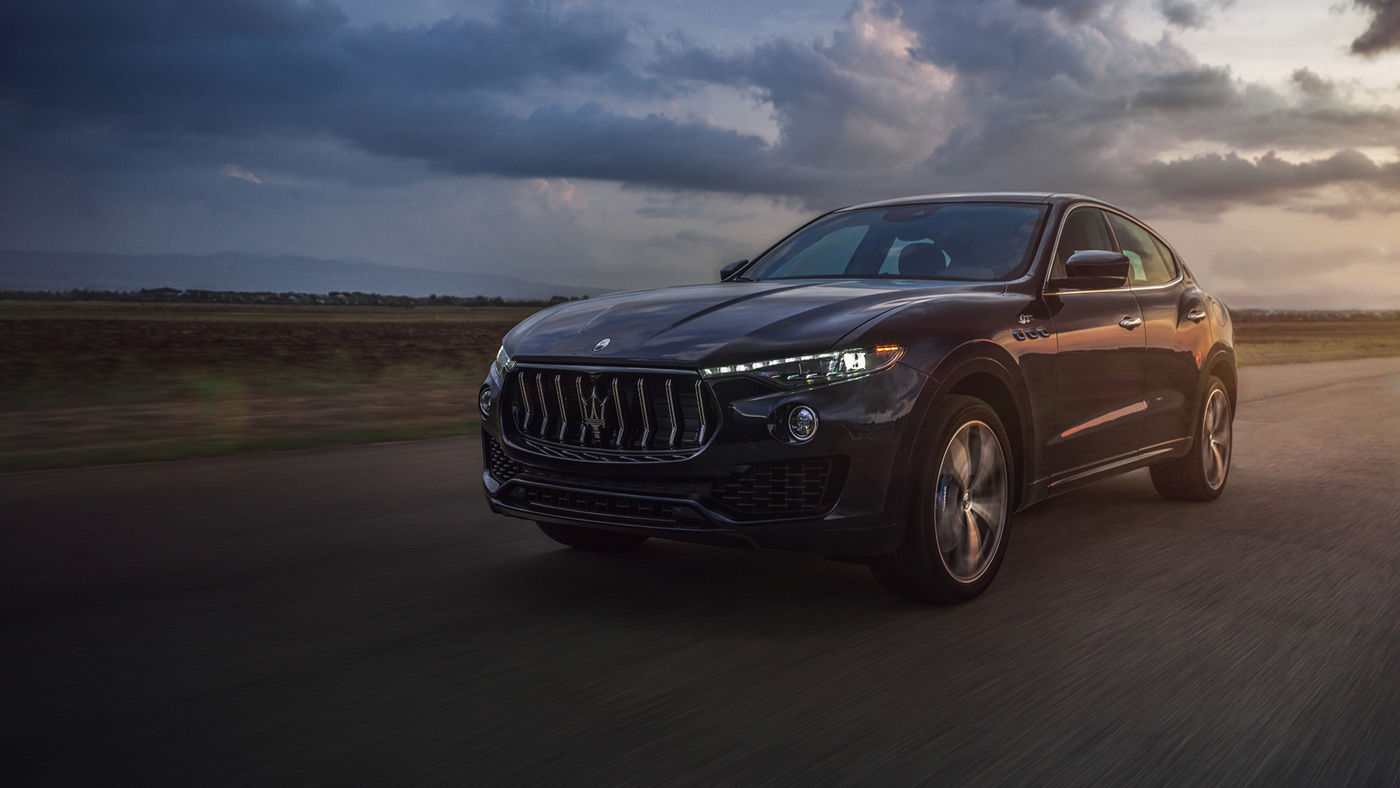
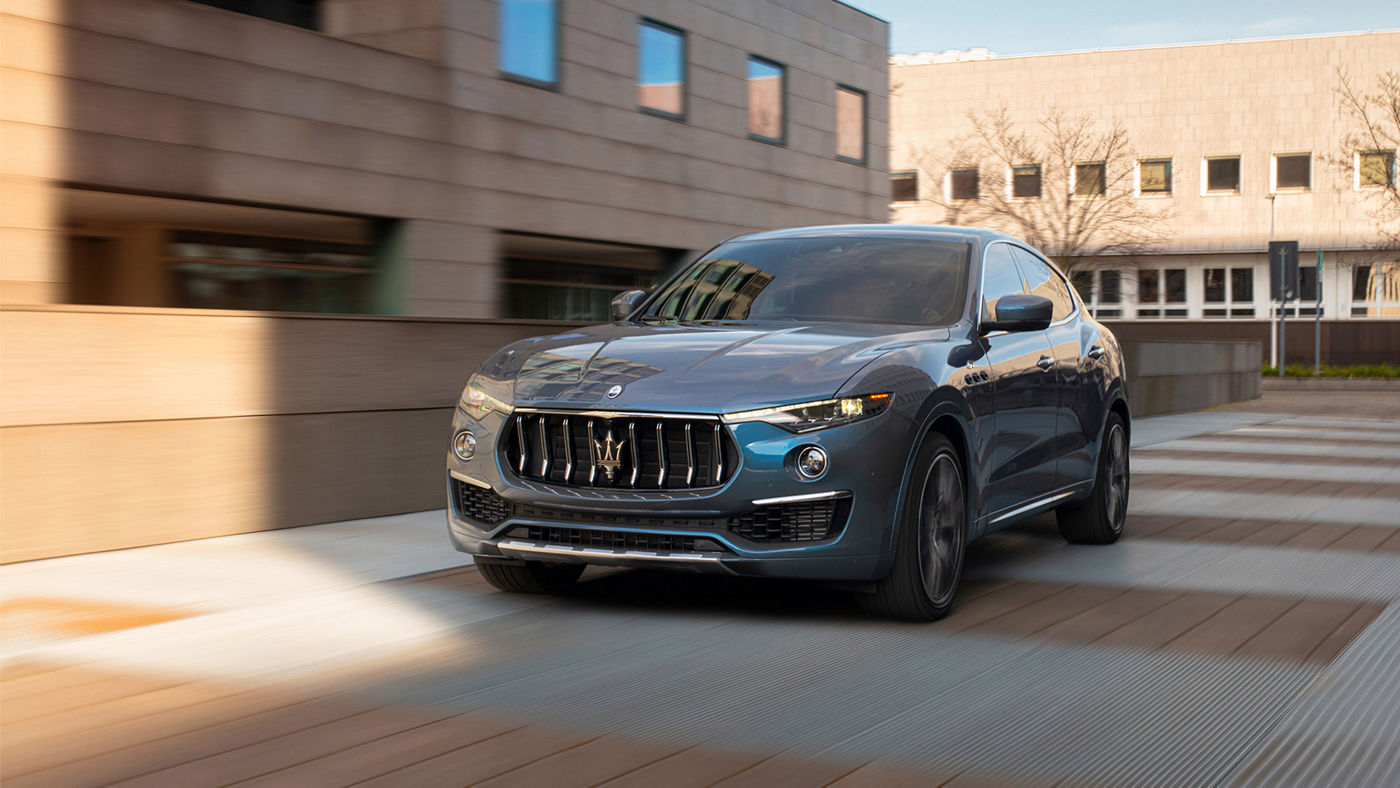
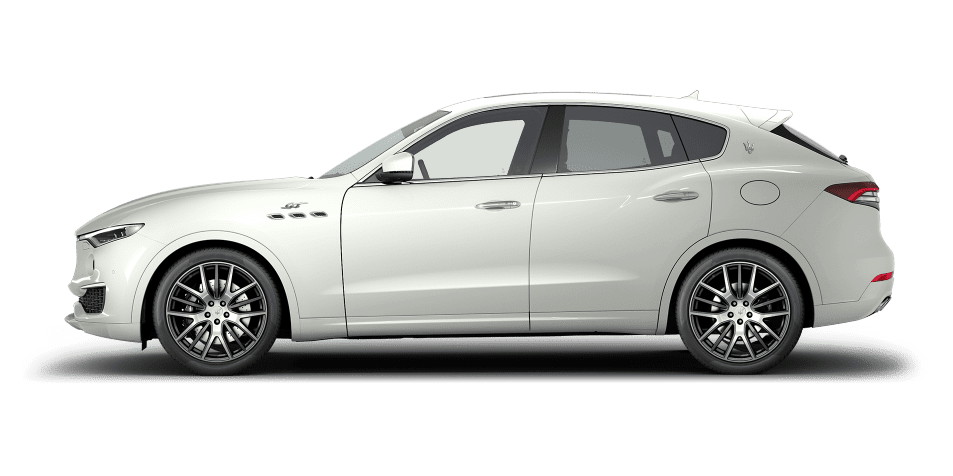
Levante
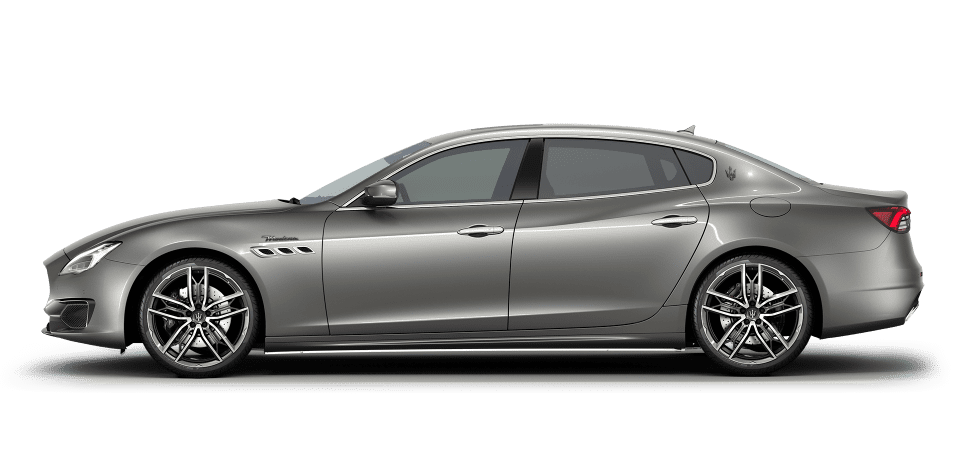
Quattroporte
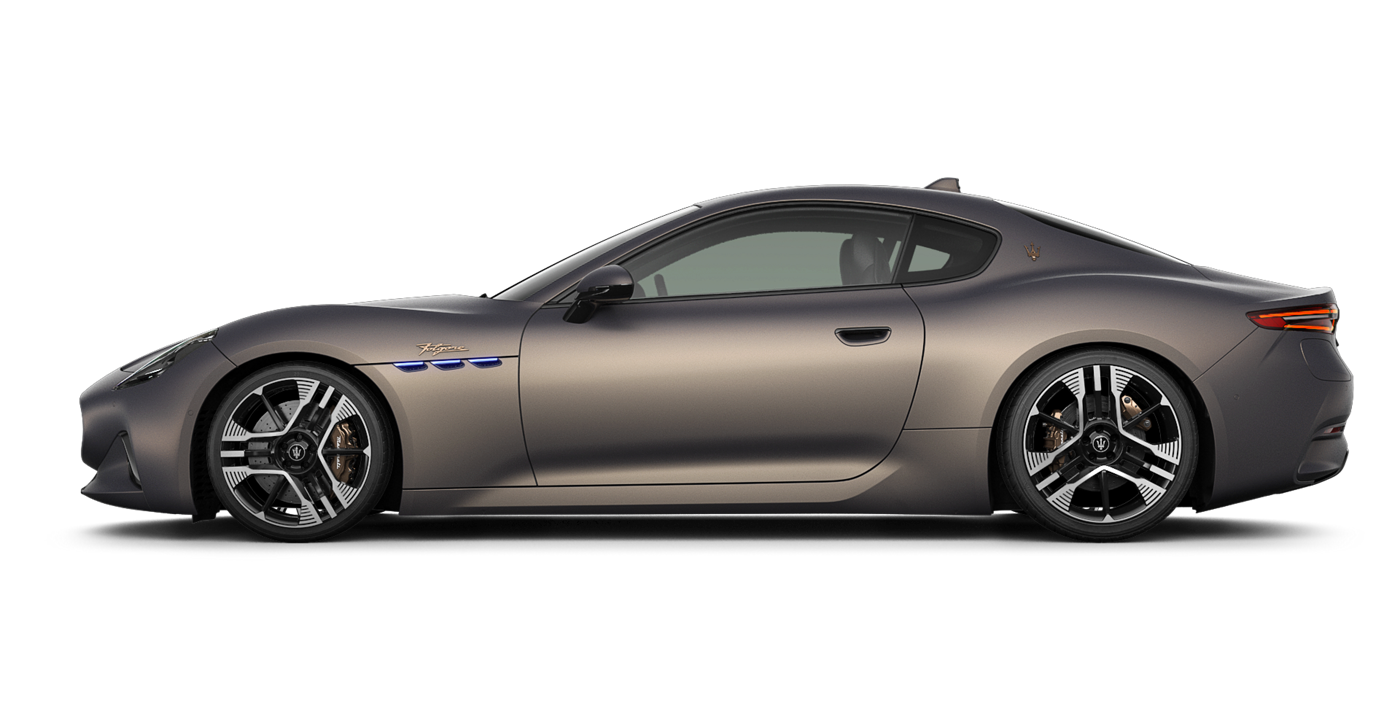
GranTurismo
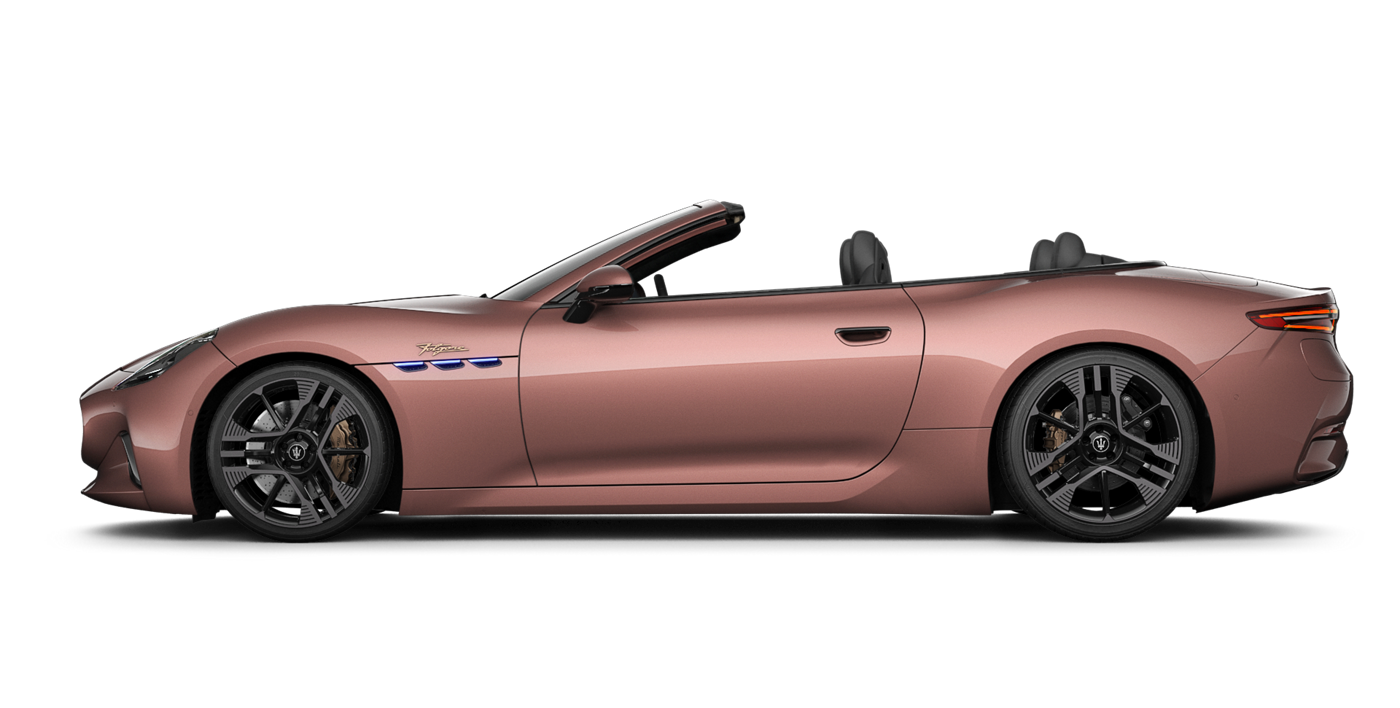
GranCabrio
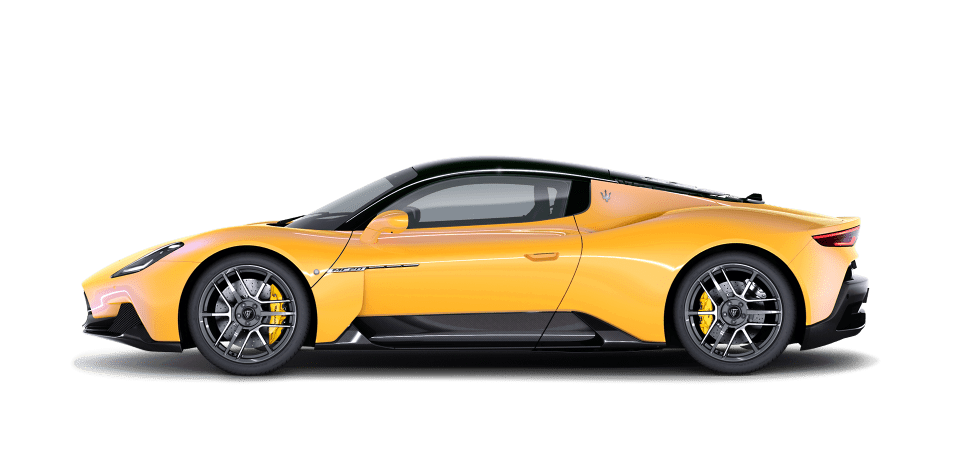
MC20
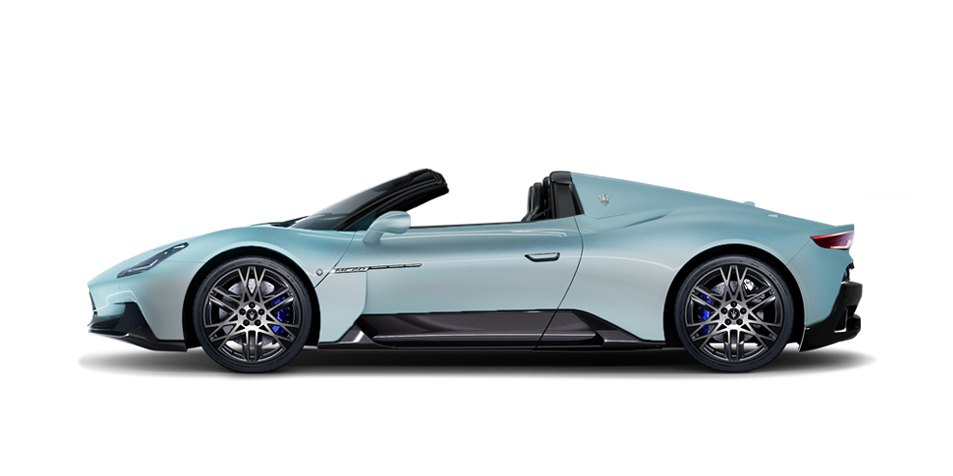
MC20 Cielo
Folgore
Fuoriserie
Special Series

Everyday Exceptional
A partire da
CHF 97.900
Velocità Massima
Accelerazione
Accelerazione
Potenza




Come nessun'altra
Velocità Massima
Accelerazione
Accelerazione
Potenza
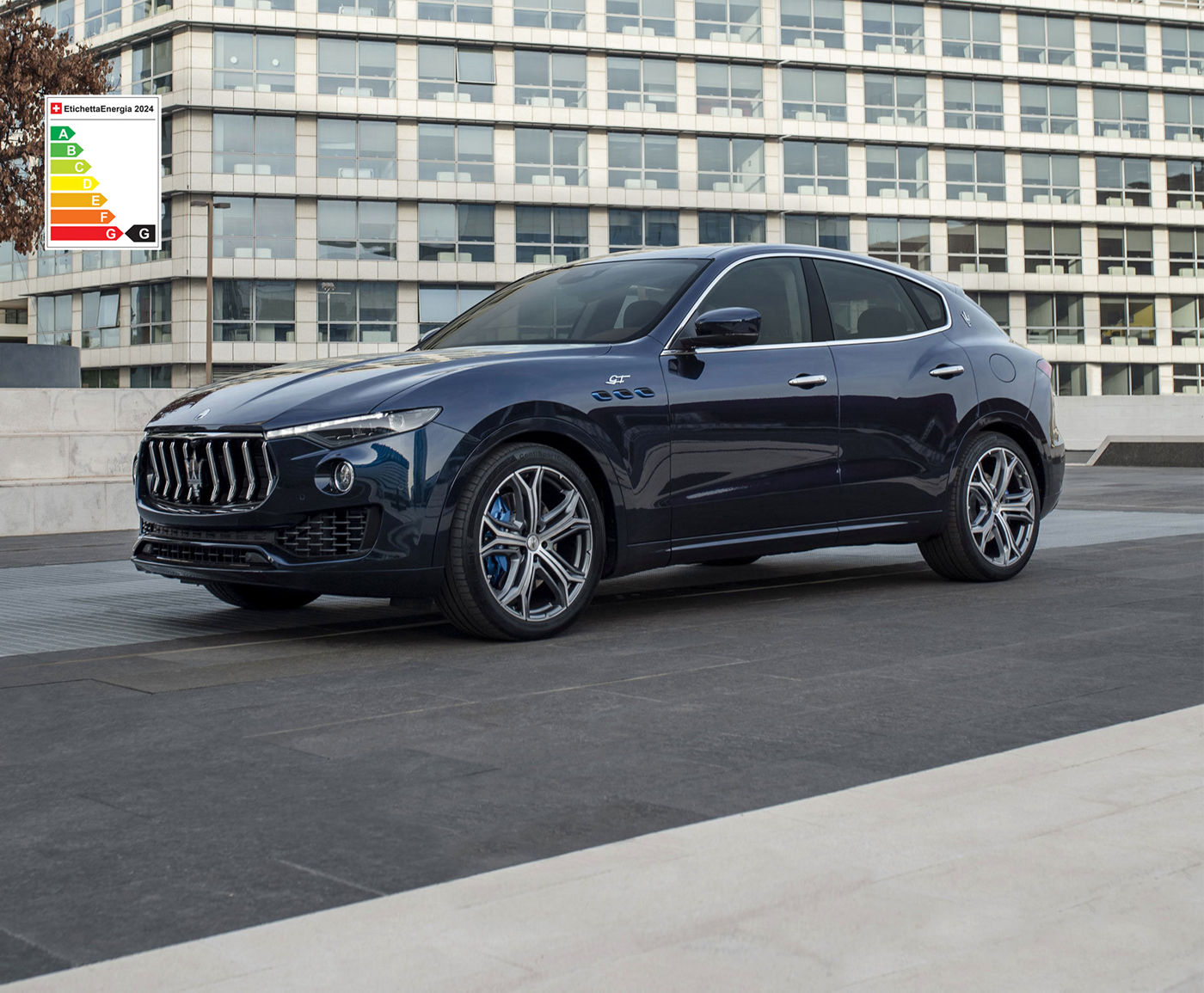




The Maserati of SUVs
Velocità Massima
Accelerazione
Accelerazione
Potenza




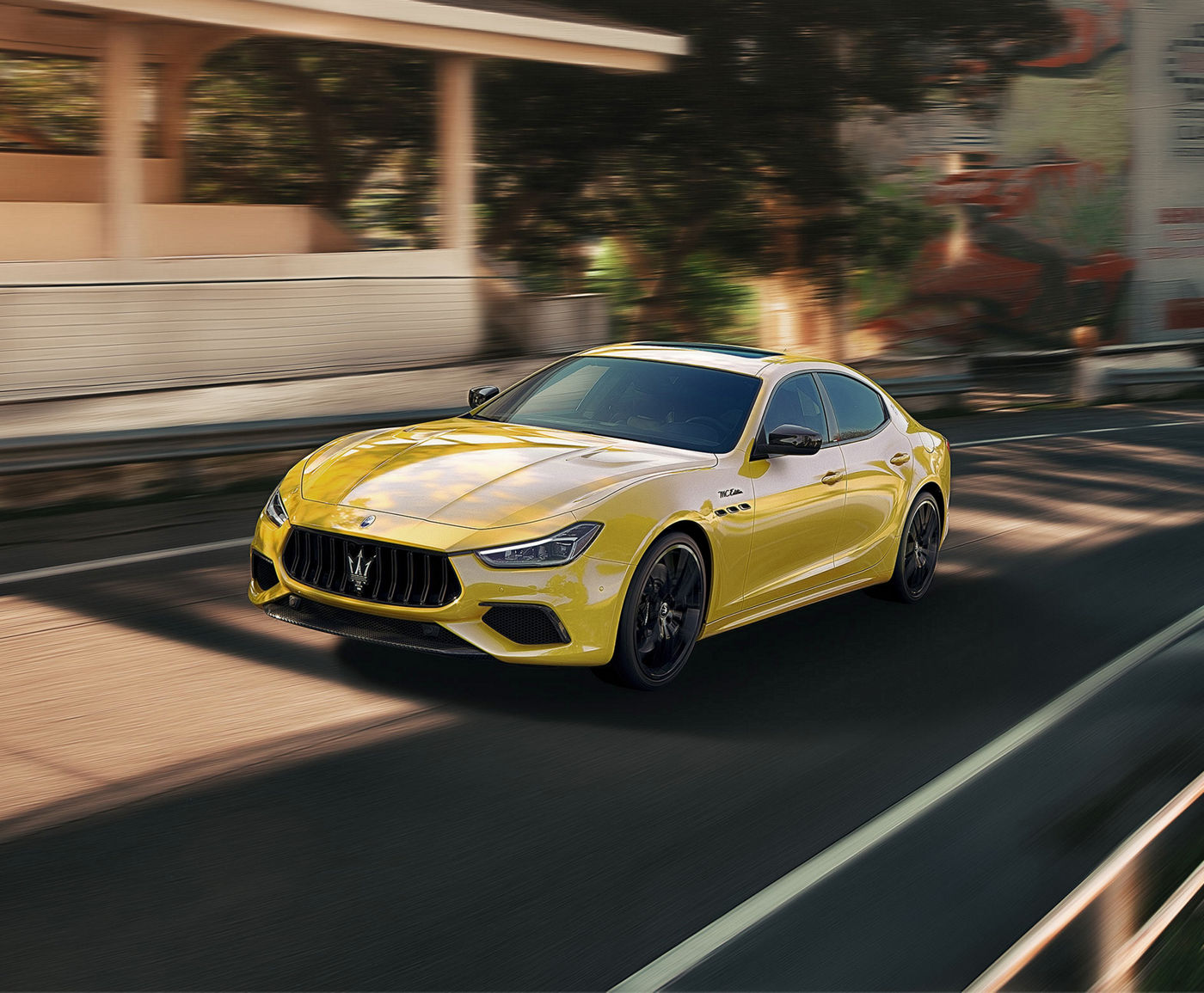
Un'icona di eleganza italiana
Velocità Massima
Accelerazione
Accelerazione
Potenza




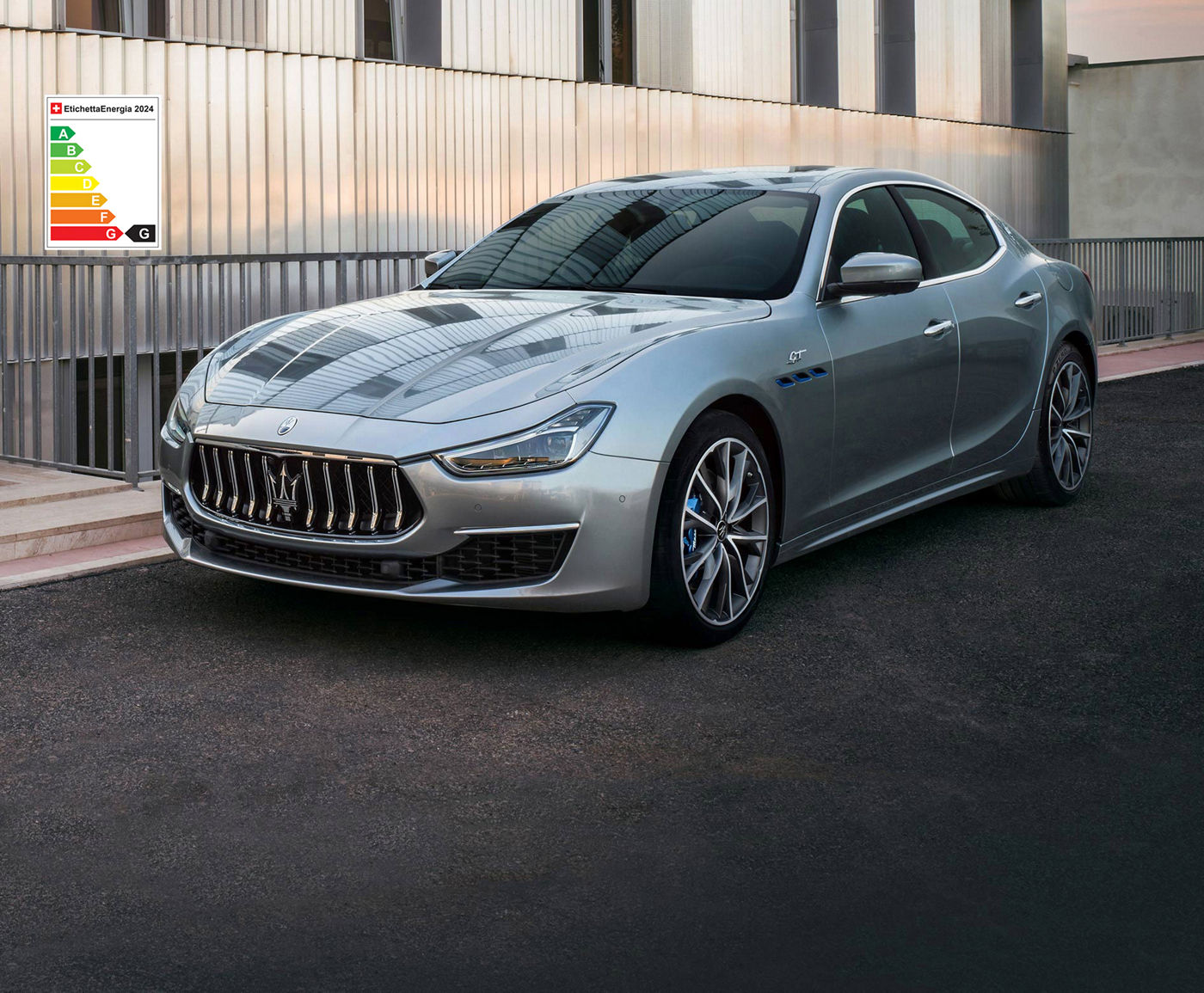
The Others Just Travel.
A partire da
CHF 203.100
Velocità Massima
Accelerazione
Accelerazione
Potenza
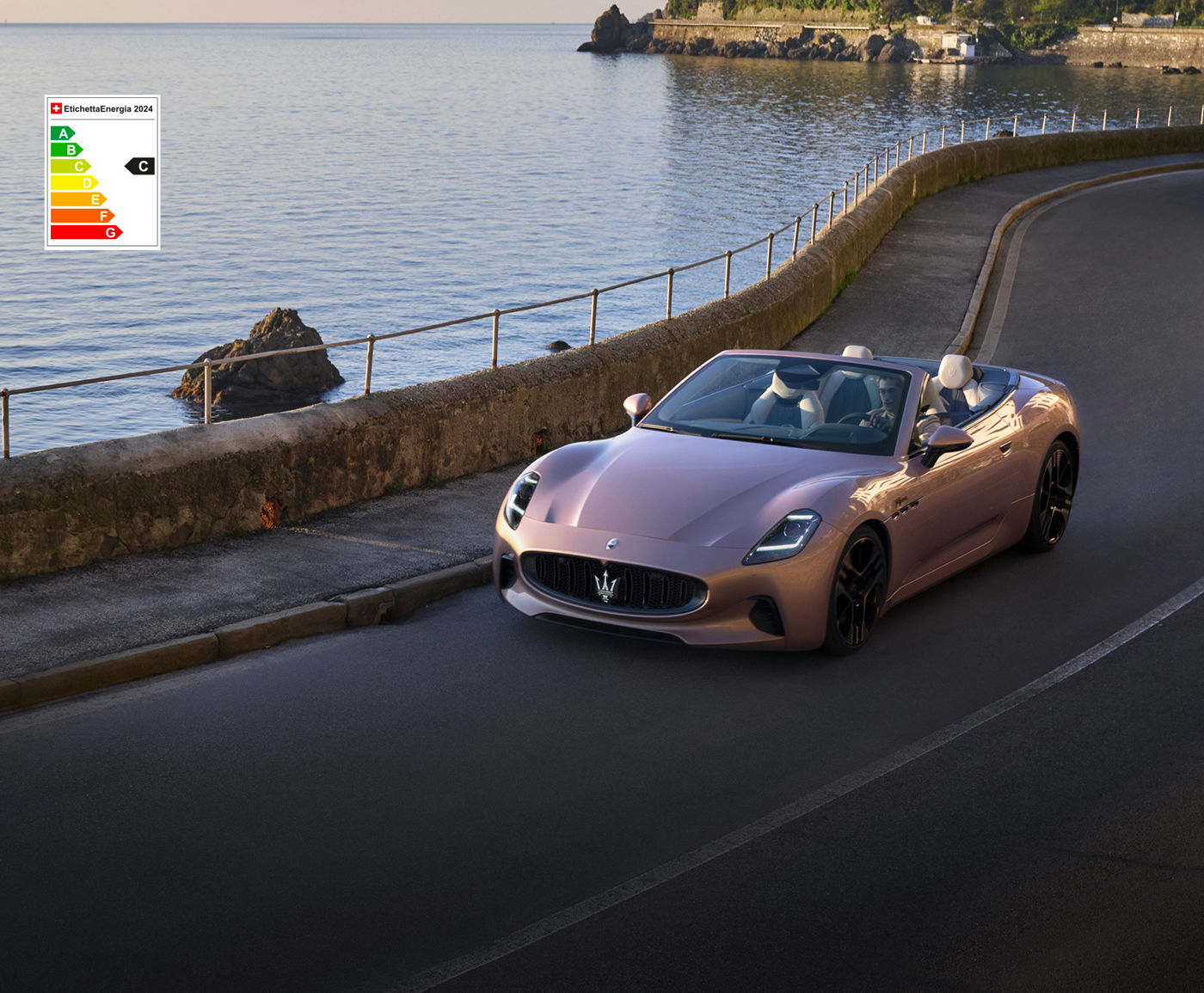




Drive Like the Best Is Yet to Come
A partire da
CHF 232.500
Velocità Massima
Accelerazione
Accelerazione
Potenza
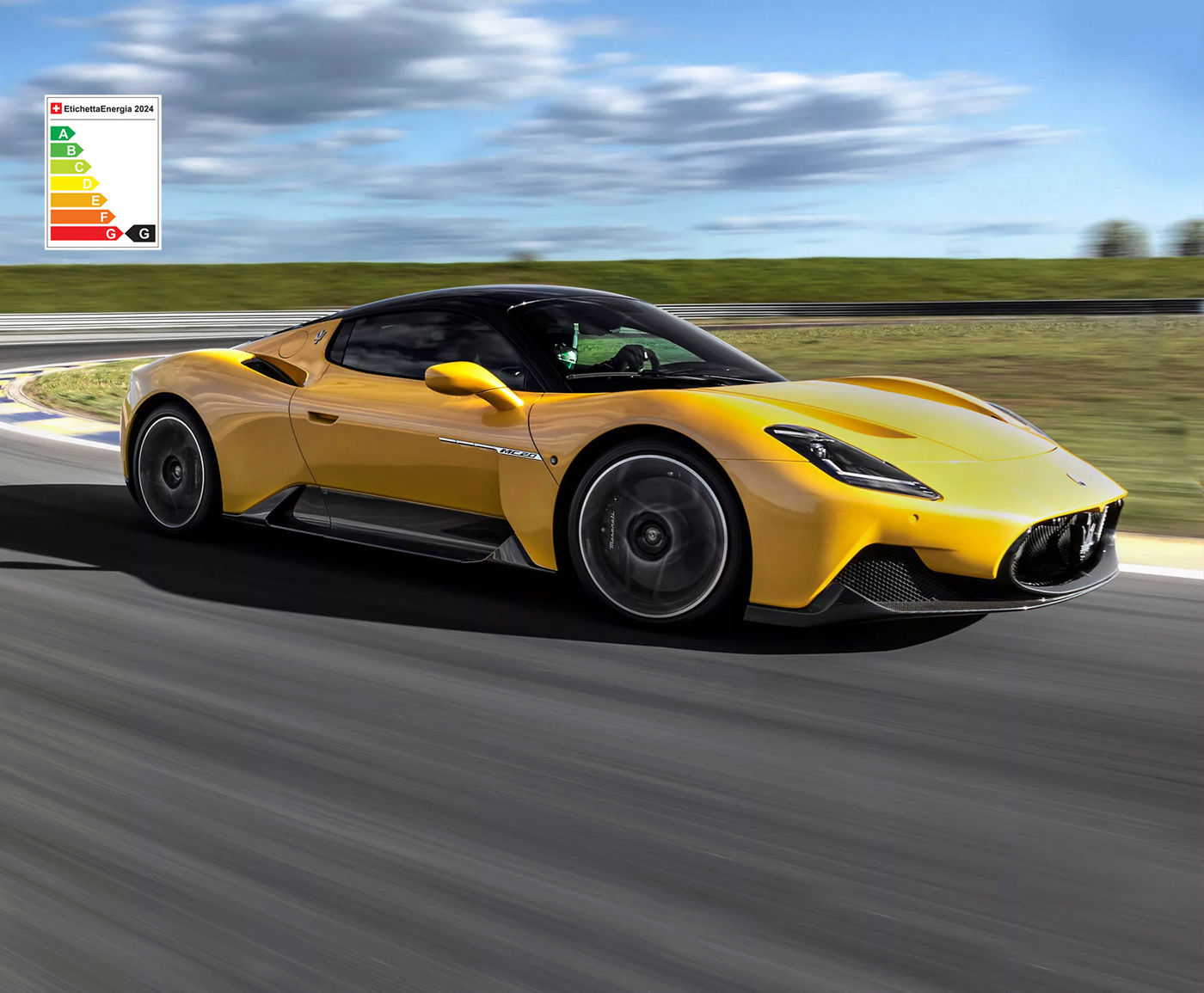




The First of Its Kind
Velocità Massima
Accelerazione
Accelerazione
Potenza
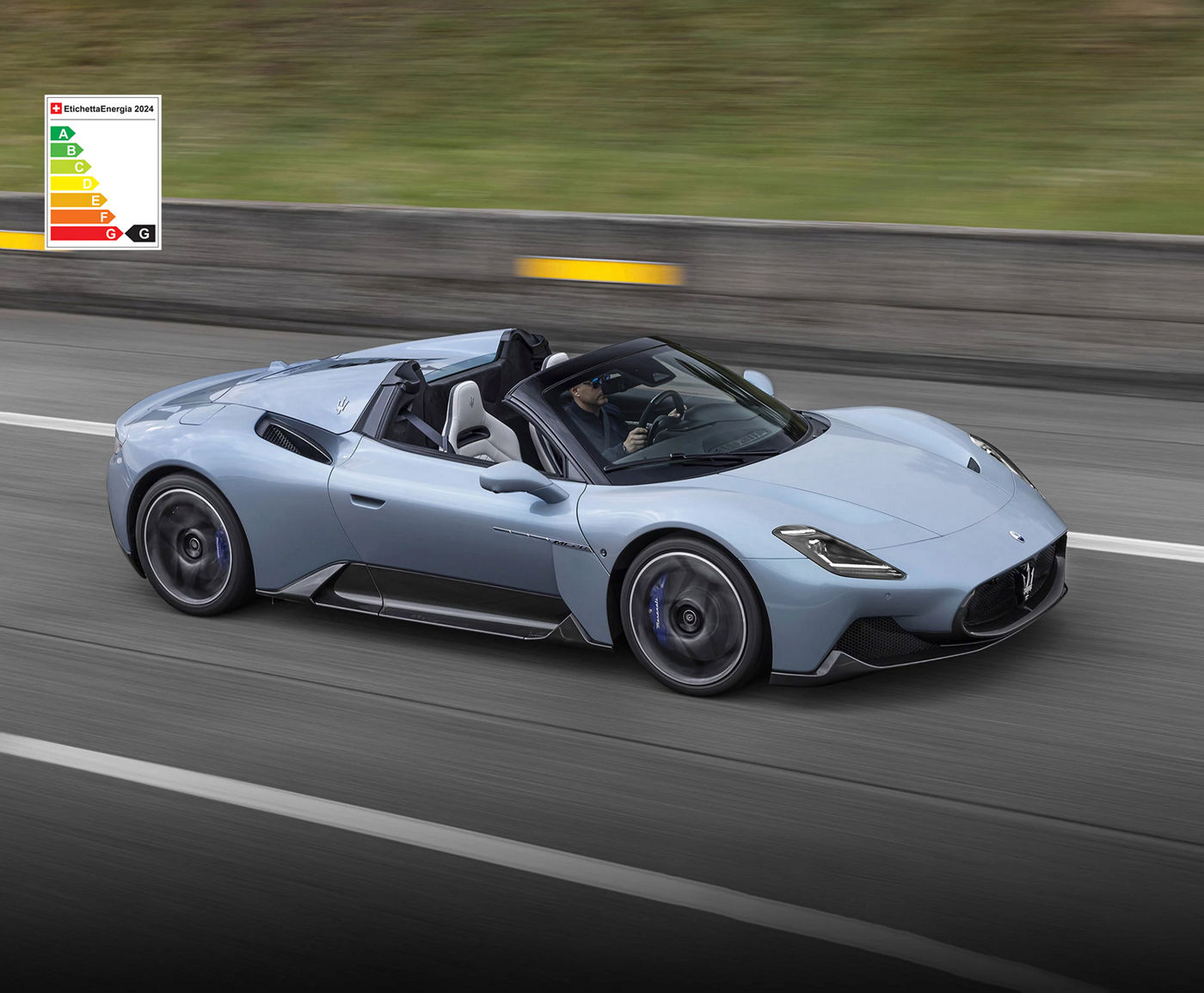




The Others Just Travel.
Velocità Massima
Accelerazione
Accelerazione
Potenza



History
Stories of Audacity
Maserati Tridente
Fuoriserie
Corse
Legacy
Experiences
Store
Partners
Values
Maserati Connect
Maserati Heritage
Servizi Finanziari
Usato Garantito
Servizi e Assistenza
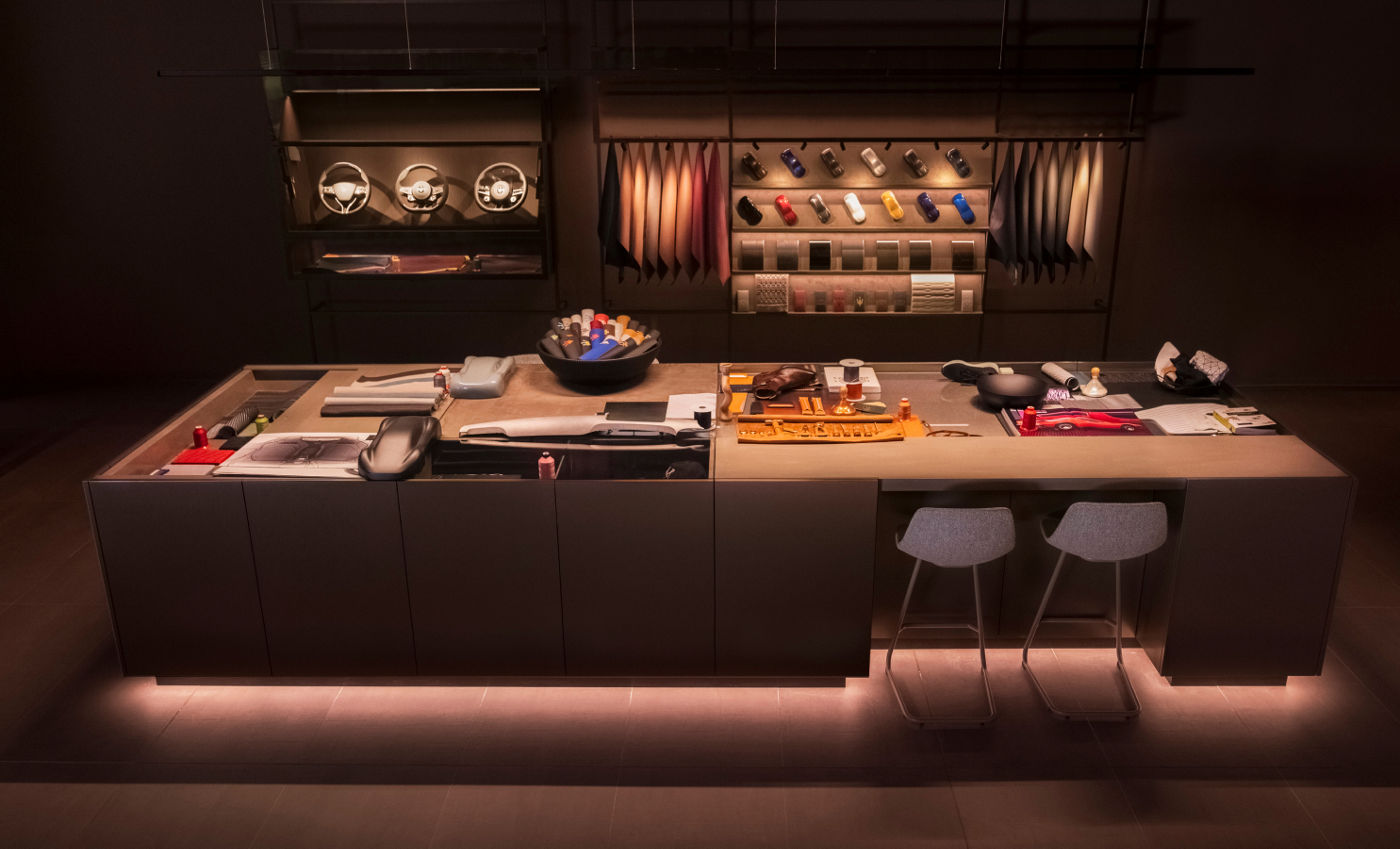
Personalizzazione